Understanding the body’s inflammatory response and ways to soothe the skin
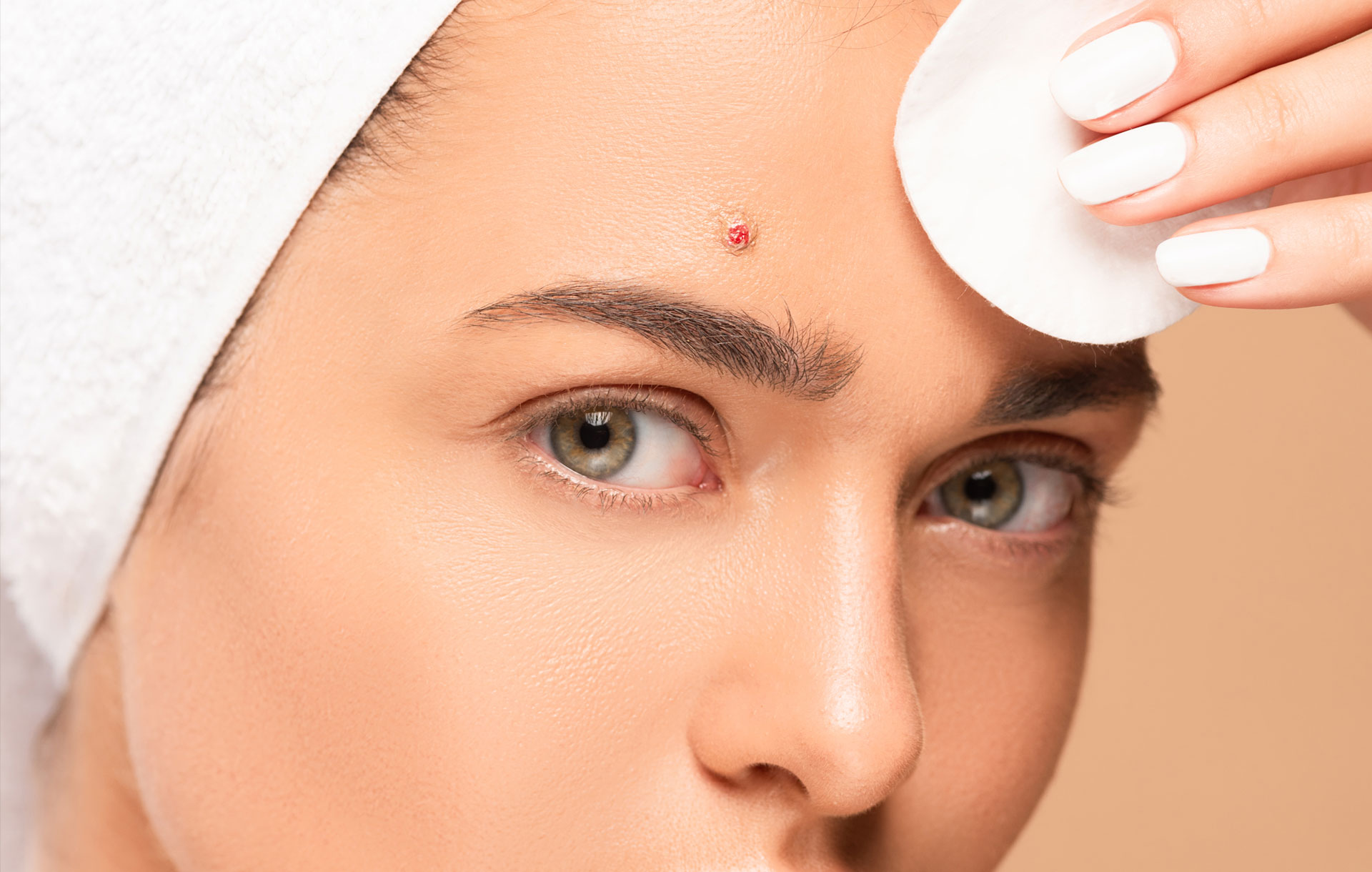
Skin inflammation is a commonly recognized symptom of aggressors affecting our skin or body. It is mostly characterized by redness, swelling, tenderness, or warmth. Not every inflammatory response looks the same. Inflammation is caused by the body’s immune system reacting to an unknown or aggravating substance. It can be brought on due to skincare ingredients, food sensitivities, or environmental aggressors. It affects nearly everyone at one time or another regardless of age, skin type, or lifestyle.
Skin inflammation has many causes, whether introduced topically, through ingestion, or by just being exposed to environmental irritants. Skin is affected mainly by the products and procedures we apply and do. Typically, skin inflammation means that the natural microbiome and the skin’s acid mantle have been disrupted. It can also indicate that the body overproduces white blood cells to remove an irritant but is causing more harm than good.
“Inflammation is caused by the body’s immune system reacting to an unknown or aggravating substance. It can be brought on due to skincare ingredients, food sensitivities, or environmental aggressors.”
[ihc-hide-content ihc_mb_type=”show” ihc_mb_who=”2,4,5,6,7″ ihc_mb_template=”3″ ]
The Causes of Inflammation in the Body
Let us look into some of the causes of inflammation. UV light and blue light cause inflammation by creating warmth and skin cell damage by breaking down collagen, elastin, and DNA. Some common dietary irritants are dairy, sugar, red meats, processed foods, caffeine, and alcohol. As the foods digest, they can release inflammation messengers in the body that can cause widespread or chronic inflammation. Underlying conditions such as rosacea or acne can cause the skin to be more sensitized and reactive. Environmental triggers can be pollution, allergies, or free radicals. The most significant contributors to skin inflammation are the products and procedures we apply and go through.
With the growing skincare industry as well as influencer skin trends, things can go awry quickly. One thing that can contribute to inflammation is the improper layering of products. Say mixing vitamin C and retinol and using products with high levels or fragrances, or applying too strong of a product without first building up a tolerance—for example, going straight for that 1% retinol without ever using retinol before. Improper usage of products not made for the face and harsh essential oils can cause inflammation too.
Now would also be a good time to mention that there are some useful applications of inflammation. Most advanced aesthetic procedures such as micro-needling, laser treatments, microcurrent, etc., result in younger-looking skin by creating a healing response that increases circulation and the creation of collagen, among other things. However, it is when this inflammation is not controlled and allowed to continue that damage is created by causing the body to attack itself. Chronically inflamed skin can lead to psoriasis, dermatitis, rosacea, fine lines, wrinkles, and collagen and elastin breakdown.
How to Treat Inflammation in the Skin
Inflammation can be treated by applying soothing products, ingesting anti-inflammatory foods, and making some lifestyle changes. Ceramides, niacinamide, sulfur, chamomile, aloe, and oatmeal are some common soothing ingredients. Antioxidants such as vitamin C, E, and D are good at reducing inflammation inside and out of the body. Anti-inflammatory foods include ginger, green tea, turmeric, dark chocolate, dark leafy greens, and berries. Avoiding over-exfoliation, using harsh exfoliants, stripping soaps, excessive sun exposure, and drinking more water are a few lifestyle changes that can help with inflammation. Suppose your client has chronic inflammation or inflammation that does not diminish with product application. In that case, they should consult their dermatologist to ensure that there isn’t something more happening beneath the surface.
[/ihc-hide-content]